ERP Solutions for Business
In today’s fast-paced digital economy, organizations of all sizes face the same fundamental challenge: how to manage their resources, processes, and data effectively while remaining competitive. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions have emerged as a cornerstone of modern business management, enabling companies to streamline operations, integrate different functions, and make more informed decisions. This article explores the concept of ERP solutions for business, their benefits, challenges, and how companies can successfully adopt them to gain long-term advantages.
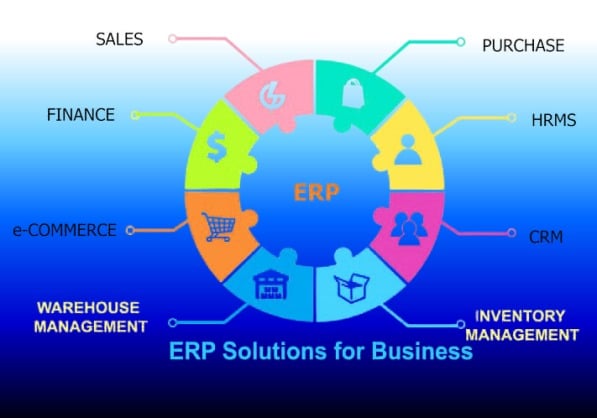
Understanding ERP Solutions
ERP solutions are integrated software platforms that unify various core business functions into one system. Traditionally, businesses managed different departments—such as finance, human resources, sales, manufacturing, and supply chain—using separate applications that rarely communicated with each other. This created silos of information, inefficiencies, and costly errors.
With ERP, all these functions operate on a shared database and interface. For example, when a sales team enters a new customer order, the data is instantly available to the inventory, procurement, and finance teams. This real-time visibility helps organizations respond faster to changes, minimize duplication of work, and ensure data consistency.
Key Features of ERP Solutions
While ERP software varies by vendor and industry focus, some common features define most modern ERP systems:
-
Financial Management – Provides tools for accounting, budgeting, expense tracking, and financial reporting.
-
Human Resources (HR) – Covers recruitment, payroll, performance management, and employee self-service.
-
Supply Chain & Inventory Management – Tracks stock levels, optimizes purchasing, and manages logistics.
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) – Helps manage customer interactions, sales opportunities, and marketing campaigns.
-
Manufacturing & Production Planning – Assists with scheduling, quality control, and resource allocation.
-
Analytics & Reporting – Offers dashboards, real-time insights, and data visualization for decision-making.
Modern ERP solutions are also cloud-based, offering mobility, scalability, and lower upfront costs compared to traditional on-premise systems.
Benefits of ERP Solutions for Business
Implementing an ERP system can transform an organization in multiple ways:
1. Improved Efficiency
By automating repetitive tasks and integrating workflows, ERP reduces manual effort and errors. Employees spend less time on data entry and more time on strategic tasks.
2. Real-Time Data Visibility
Executives can access up-to-date information on finances, operations, and customer activity. This visibility improves decision-making and forecasting accuracy.
3. Cost Savings
Though ERP requires initial investment, businesses often save money long term through reduced operational inefficiencies, lower inventory costs, and optimized resource allocation.
4. Enhanced Customer Experience
ERP systems provide a 360-degree view of customers. Sales and service teams can access order histories, preferences, and support tickets, which leads to better customer service.
5. Scalability
As businesses grow, ERP solutions can be customized and scaled to handle increased demand, new product lines, or expansion into new markets.
6. Regulatory Compliance
ERP systems help businesses comply with financial regulations, data protection standards, and industry-specific requirements through accurate record-keeping and audit trails.
ERP for Different Business Sizes
Small Businesses
For small businesses, ERP solutions may seem unnecessary at first. However, cloud-based ERP platforms with modular pricing make it possible for startups to access enterprise-grade tools without high upfront costs. Small businesses benefit from ERP by reducing paperwork, improving cash flow management, and streamlining daily operations.
Medium Enterprises
Mid-sized organizations often struggle with growing complexity. An ERP system provides the structure and automation necessary to scale operations efficiently. For instance, a medium-sized manufacturing company may use ERP to synchronize production schedules with supplier deliveries and customer orders.
Large Corporations
Large enterprises require robust ERP systems with advanced features, customization, and integration capabilities. Global corporations often use ERP to standardize operations across different regions while maintaining compliance with local laws. Vendors like SAP, Oracle NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 cater to such large-scale requirements.
Industry-Specific ERP Applications
Different industries have unique needs, and ERP vendors often offer tailored solutions:
-
Manufacturing: Tools for production scheduling, quality assurance, and shop-floor automation.
-
Retail & E-commerce: Inventory management, demand forecasting, and multi-channel integration.
-
Healthcare: Patient management, billing, and regulatory compliance features.
-
Construction: Project management, procurement, and workforce tracking.
-
Education: Student information systems, admissions, and financial planning.
This industry-specific customization ensures ERP delivers maximum value by addressing the challenges unique to each sector.
Challenges in Implementing ERP
While ERP solutions are powerful, implementation is not without hurdles. Businesses often face:
-
High Initial Costs – ERP can be expensive, especially for on-premise deployments requiring hardware and IT staff.
-
Resistance to Change – Employees may resist adopting new systems, preferring legacy tools.
-
Complexity – Implementing ERP often requires significant time, training, and process re-engineering.
-
Data Migration – Transferring data from old systems to ERP can be complicated and risky.
-
Customization Issues – Over-customizing ERP may lead to difficulties in upgrades and vendor support.
Successful implementation requires careful planning, stakeholder buy-in, and choosing the right vendor that matches business goals.
Future Trends in ERP Solutions
ERP solutions are evolving rapidly in response to new technologies and business needs. Some key trends include:
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Predictive analytics for demand forecasting, customer insights, and anomaly detection.
-
Mobile ERP: Access to ERP data on smartphones and tablets, enabling greater flexibility for remote work.
-
IoT Integration: Connecting ERP with Internet of Things devices to track equipment performance, inventory movement, and production metrics.
-
Blockchain: Enhancing supply chain transparency and secure transactions.
-
Low-Code Customization: Allowing businesses to configure ERP solutions without heavy coding or IT involvement.
These advancements make ERP solutions smarter, more accessible, and better aligned with digital transformation strategies.
Choosing the Right ERP Solution
Selecting the right ERP is critical for business success. Factors to consider include:
-
Business Goals: Does the ERP align with long-term growth and strategic priorities?
-
Deployment Type: Cloud vs. on-premise solutions depending on budget, scalability, and IT infrastructure.
-
Vendor Reputation: Established vendors offer reliability, while smaller vendors may provide niche innovations.
-
Integration Capabilities: ERP should integrate seamlessly with existing tools such as CRM or e-commerce platforms.
-
User Friendliness: A user-friendly interface increases employee adoption and reduces training time.
Many businesses begin with pilot programs or phased rollouts to minimize risk and adapt gradually.
Conclusion
ERP solutions have become indispensable for modern businesses striving to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. By integrating diverse business processes into a single system, ERP provides the clarity and control needed to thrive in an increasingly complex environment.
While challenges such as cost and complexity exist, the long-term benefits outweigh the risks. With emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and mobile access shaping the future of ERP, companies that adopt the right system today will be better prepared for tomorrow’s business landscape.
In essence, ERP is not just software—it is a strategic investment that empowers businesses to work smarter, scale faster, and compete more effectively in the global marketplace.